Standard Thermostat Wiring is a crucial aspect of any HVAC system, ensuring that the thermostat can communicate effectively with the heating and cooling components of the system. Understanding how thermostat wiring works is essential for proper installation and troubleshooting.
Importance of Standard Thermostat Wiring
Standard Thermostat Wiring plays a vital role in controlling the temperature in a home or building. Properly wired thermostats ensure that the heating and cooling systems operate efficiently, saving energy and maintaining comfort levels. Without correct wiring, the thermostat may not function correctly, leading to issues such as inconsistent temperatures or system malfunctions.
Reading and Interpreting Standard Thermostat Wiring
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the color-coding used in thermostat wiring. Different wires are designated for specific functions, such as power, heating, cooling, and fan control.
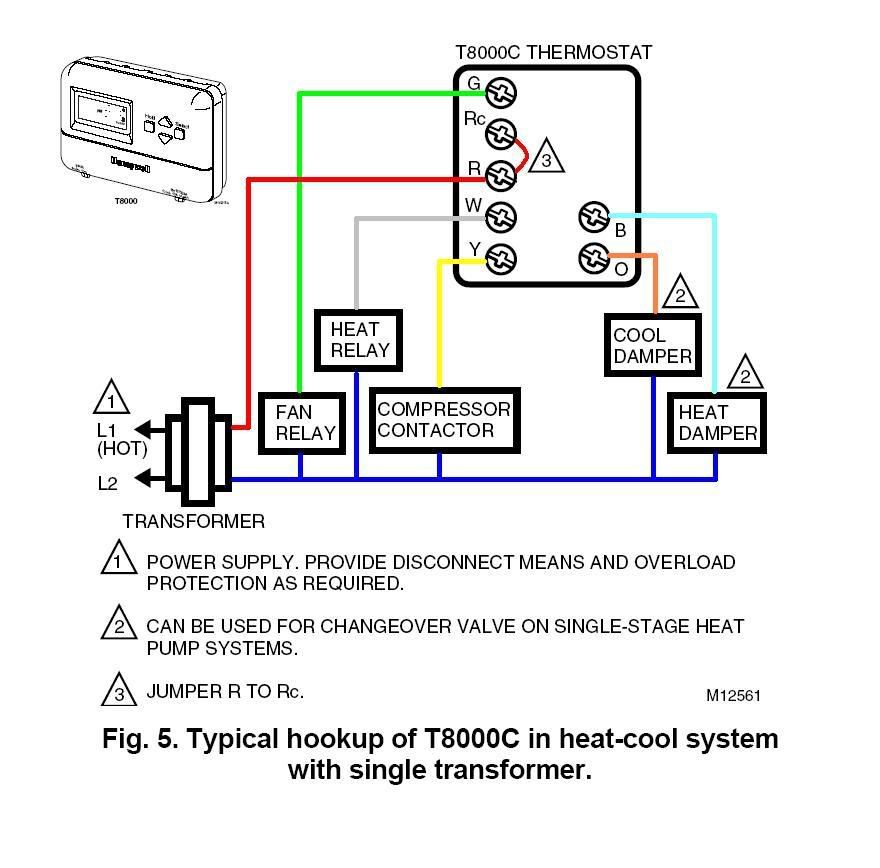
- Refer to the wiring diagram provided by the thermostat manufacturer. This diagram will outline how each wire should be connected to the corresponding terminals on the thermostat and HVAC system.
- Use a multimeter to test the continuity of wires and ensure that the connections are secure. A faulty connection can lead to system malfunctions.
Using Standard Thermostat Wiring for Troubleshooting
- Check for loose or damaged wires that may be causing connectivity issues. Tighten connections or replace damaged wires as needed.
- Verify that the wires are connected to the correct terminals on both the thermostat and HVAC system. Incorrect wiring can result in system malfunctions or damage.
- Use a wiring diagram to trace the flow of electricity through the system and identify any potential points of failure. This can help pinpoint the source of electrical problems.
Safety Considerations
When working with Standard Thermostat Wiring, it is essential to prioritize safety. Follow these tips to ensure a safe working environment:
- Always turn off the power supply before working on thermostat wiring to prevent electrical shock.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling wiring components.
- Avoid working on wiring in wet or damp conditions to reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
Standard Thermostat Wiring
Guide to wiring connections for room thermostats

Heat Pump Thermostat Wiring Diagram Honeywell
Wiring A Thermostat To A Furnace / Furnace Thermostat Wiring and

Thermostat Wiring to a Furnace and AC Unit! Color Code, How it Works

How To Install Thermostat Wiring

Thermostat Wiring Explained
