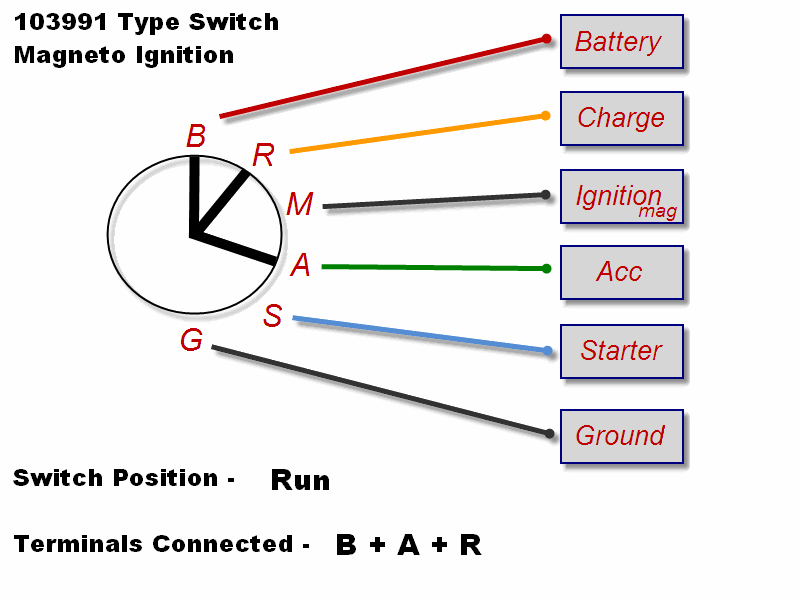
Understanding the Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram is crucial for any mechanic or DIY enthusiast working on electrical systems in vehicles. This diagram provides a visual representation of the wiring and electrical connections for the ignition switch, helping users to troubleshoot, repair, or modify the system effectively.
Importance of Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram
The Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram is essential for the following reasons:
- It helps identify the correct wiring connections for the ignition switch.
- It ensures proper installation and functioning of the ignition switch.
- It assists in troubleshooting electrical issues related to the ignition system.
Reading and Interpreting Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram
Reading and interpreting the Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram requires some basic understanding of electrical symbols and circuitry. Here are some tips to help you:
- Identify the key components such as battery, ignition switch, starter motor, and other relevant parts.
- Follow the color codes and lines connecting the components to understand the wiring connections.
- Refer to the legend or key provided in the diagram to decipher any symbols or abbreviations used.
Using Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram for Troubleshooting
When faced with electrical problems in the ignition system, the Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting. Here is how you can use it effectively:
- Identify any loose or damaged connections by comparing them to the diagram.
- Check for continuity or voltage at various points in the wiring using a multimeter.
- Trace the wiring back to the source of the issue to pinpoint the problem accurately.
Safety Tips for Working with Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram
It is essential to prioritize safety when working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams. Here are some safety tips and best practices to follow:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent short circuits or electrical shocks.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses to reduce the risk of injury.
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions to prevent electrical hazards.
Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram
Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram

indak ignition switch wiring diagram – MarilenaCalym

Indak 3 Position Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram – Free Wiring Diagram
Indak 6 Terminal Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram – Free Wiring Diagram

Indak Ignition Switch Wiring Diagram – Esquilo.io

Indak 6 Terminal Ignition Switch Diagram – Greenied